Energy-Efficient and Environmentally Friendly Auxiliary Equipment
2025-03-08 Page view:
In today’s plastic processing industry, auxiliary equipment plays a crucial role alongside the core machinery. Whether it’s extrusion, injection moulding, calendering, blow moulding, or spinning, auxiliary systems collaborate seamlessly with the main equipment to handle complex production processes. The automation, intelligence, and rational configuration of these systems are pivotal in maintaining product quality and strengthening a company’s competitive edge.
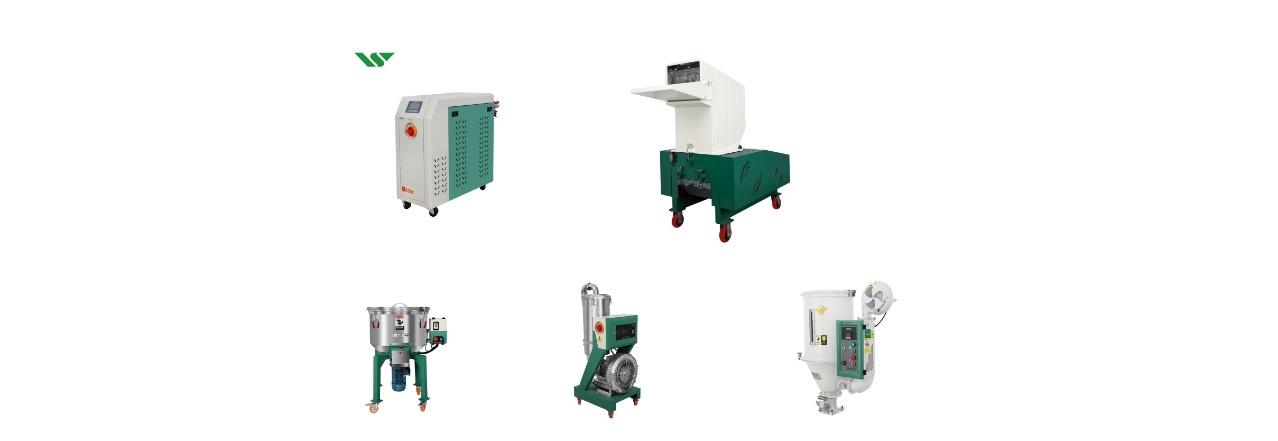

Plastic auxiliary equipment can be categorized into three main systems: the feeding system, temperature control system, and scrap recycling system.
1. Feeding System: Providing High-Quality Raw Materials for Production
The feeding system’s auxiliary equipment includes dryers, conveyors, metering devices, and mixers. Drying equipment is vital for handling moisture-sensitive materials, ensuring raw materials are at the optimal moisture level before entering the moulding process. Materials such as ABS, POM (polyoxymethylene), PC (polycarbonate), and PA (nylon) require thorough drying before moulding. Certain polyolefins, such as random copolymer polypropylene (PP-R) and cross-linked polyethylene (PE), also demand efficient drying to guarantee the quality of the finished product.
Different materials require different types of dryers. For example, pellet materials like fillers and PVC are often dried using oven-type dryers, while heat-sensitive materials are best dried with a rotating double-cone vacuum dryer. For continuous production, hopper dryers are ideal.
In terms of conveying, powder materials are typically transported using spring tube conveyors or Roots blower-based pneumatic systems, while pellet materials are conveyed with vacuum feeders. Centralized feeding systems are commonly used in automated and large-scale production, employing computer-integrated control to ensure accurate metering and proportional delivery, thereby enhancing efficiency and consistency in production.

2. Temperature Control System: Ensuring Stable Product Quality
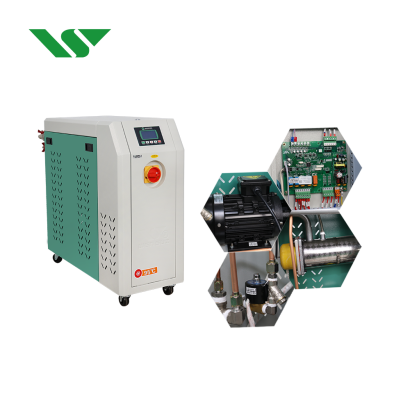
Precise temperature control is crucial in plastic processing, particularly in processes like extrusion, injection moulding, and calendering. The temperature of the barrel, mould, and calendering rollers is key to achieving consistent product quality. Modern temperature control systems typically use thermal oil heating, while more complex processes often use steam heating.
Mould temperature controllers are essential in injection moulding, helping regulate the mould temperature to ensure product precision. Cooling equipment usually employs air or water cooling systems, with water cooling being more widely used due to its superior heat exchange capacity. While air cooling is more convenient, it is less efficient in heat transfer.

3. Scrap Recycling System: Reducing Production Costs and Enhancing Resource Utilisation
Recycling scrap materials during plastic processing is an effective way to lower production costs and increase resource efficiency. Scrap materials typically account for 5% to 20% of the total production volume, making efficient scrap recovery a key factor in boosting a company’s competitiveness.
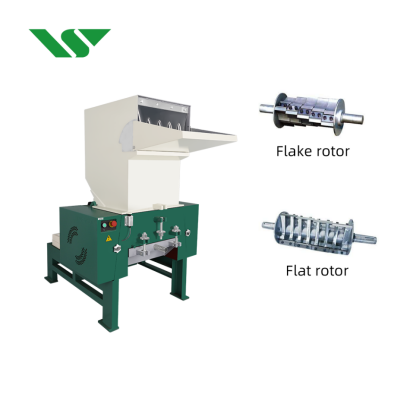
Plastic crusher shredders are widely used in scrap recovery, with equipment chosen based on the type of scrap and the processing requirements. For example, rigid and small-volume products use specialized shredders, while soft plastic foams require different recycling pelletizers. For longer products such as pipes and profiles, shredders that can directly crush and pelletize are ideal. Pelletizing machines are used for recycling waste filaments.
Modern plastic recycling equipment is increasingly designed to be low-noise, easy to operate, and equipped with continuous tubular conveyors. These innovations not only boost productivity but also reduce environmental impact, aligning with eco-friendly standards.
By optimizing the configuration and use of auxiliary equipment, the plastic processing industry can not only improve production efficiency and minimize resource waste but also make significant contributions to environmental protection and energy-saving initiatives. The latest auxiliary equipment is steering the industry towards greater efficiency and sustainability.



